
Video
Leading Expert In Forged Turbine Blades
Our precision forging process employs a patented optimized technique, offering the following advantages:
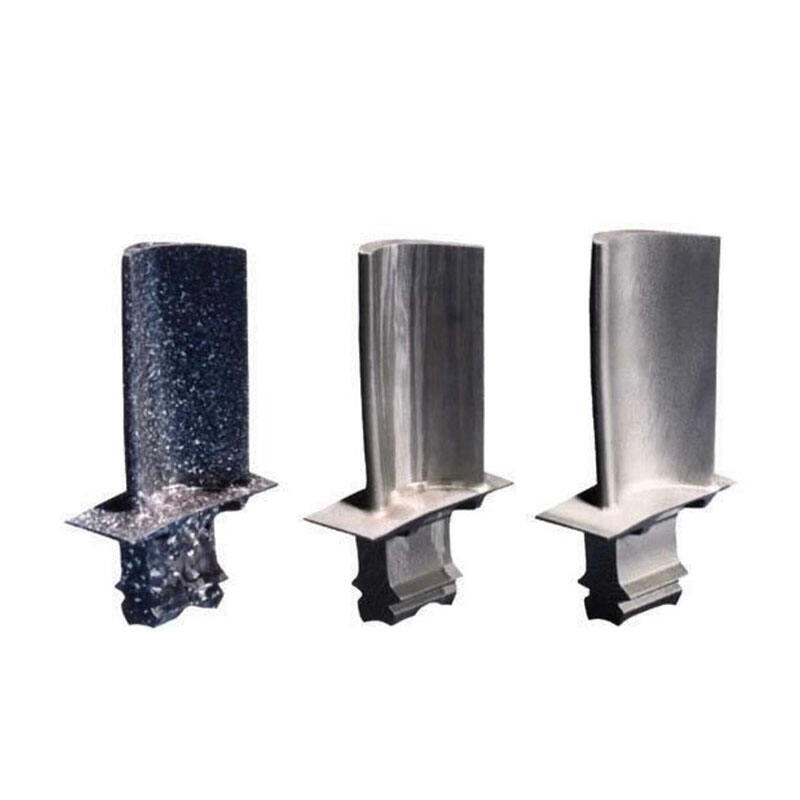
1. Ultra-Low Machining Allowance
The material allowance after precision forging is only 0.1-1mm, compared to 6-10mm for traditional precision forging. This not only reduces material costs but also significantly shortens the time required for subsequent machining processes.
2. 3-Mould Faster Production
Our production speed has also gained a substantial edge through adjustments. By using a “one-to-three” mold configuration for production, we have reduced the production time to one-third of traditional methods, which typically require one mold per product.
3. Higher Efficiency
Through technical optimization, our overall production efficiency has seen significant improvement, with total production time reduced by 70% compared to previous methods.
4. Cost-Effective
The time and material cost savings from these advantages have created room for competitive pricing. Our product is priced 50% below the market average!
Our forged turbine blades represent the industry standard for reliability and performance in demanding turbomachinery environments. Manufactured using advanced forging techniques, these components deliver superior structural integrity and operational longevity across aerospace, power generation, and industrial applications.
Key advantages:
• Structural integrity and reliability
• Extended service life and cost savings
• Proven performance and precision
• Material options for different applications
Trust factors:
• Quality control emphasis
• Industry standards compliance
• Decades of expertise
• Rigorous testing
Thermodynamic Principles
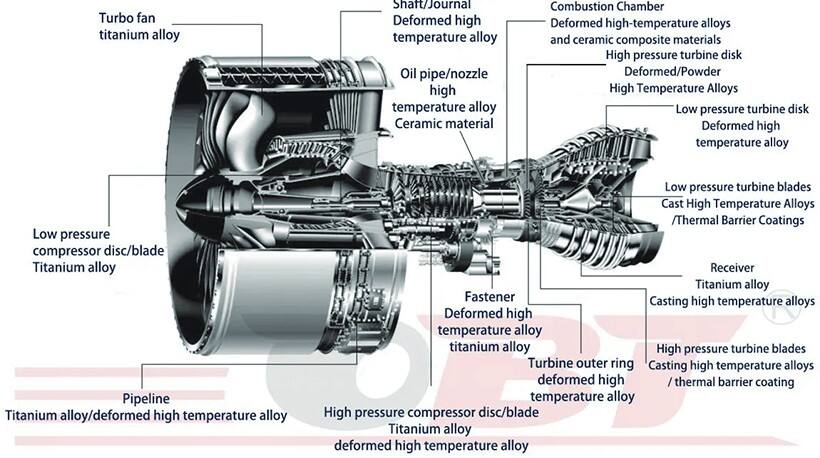
Forged blades operate in high-temperature, high-pressure, or high-speed airflow environments, requiring excellent mechanical strength and durability. The forging process refines the grain structure through metal plastic deformation, improves material density and mechanical properties, giving the blades superior fatigue resistance and structural stability. In some high-temperature applications, blades also require cooling systems that introduce cooling media to reduce blade surface temperature and maintain the stability of blade structure and material performance.
In summary, forged blades achieve energy conversion by utilizing pressure differences generated by aerodynamic principles, and ensure blade stability and durability in various working environments through forging processes and quality materials. Their design and manufacturing must fully consider aerodynamic performance, material selection, forging technology, and other factors to ensure that the blades can operate efficiently and stably for long periods.
Product Features
Load Bearing and Support
Forged blades are the main support structure for rotors or stators. The blades are fixed on the disk or casing to form a blade array. These blades generate power or achieve gas compression through airflow action, driving rotor rotation and operating related mechanical equipment.
Power Transmission
Forged blades bear centrifugal forces and aerodynamic loads, converting the kinetic energy of airflow into mechanical energy, providing power support for equipment operation. During high-speed rotation, the blades convert airflow energy into rotational kinetic energy on the shaft or achieve gas compression and pressurization.
Stable Operation
The design and manufacturing of forged blades need to ensure sufficient strength and rigidity to withstand centrifugal forces and inertial forces caused by high-speed rotation. At the same time, precise balancing and alignment are required to ensure stable equipment operation. The forging process guarantees the uniformity and density of the blade's internal structure, improving overall structural reliability.
Excellent Mechanical Properties
Forged blades obtain excellent mechanical properties through the forging process, including high strength, high toughness, and good fatigue resistance. The forging process causes metal fibers to distribute continuously along the blade shape, eliminating internal defects and improving the blade's load-bearing capacity and service life.
features

The turbine blade is the main support structurefor fixed blades. The blades are fixed on thedisk to form a rotating blade array. Theseblades generate power through the impact ofairflow, thereby pushing the turbine disk torotate and driving related mechanicalequipment to operate.
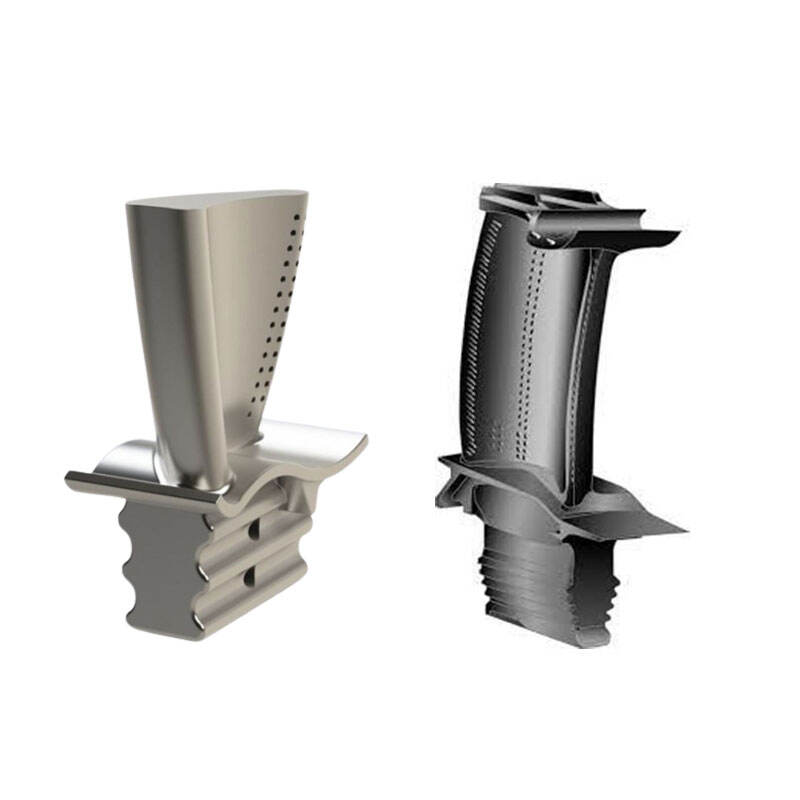

The turbine blade bears the centrifugal force andmomentum generated by the turbine blades,converts the kinetic energy of the airflow intomechanical energy, and provides power tosupport the operation of the turbine. Duringtheir high-speed rotation, they convert air flow energy into rotational kinetic energy on the shaft.
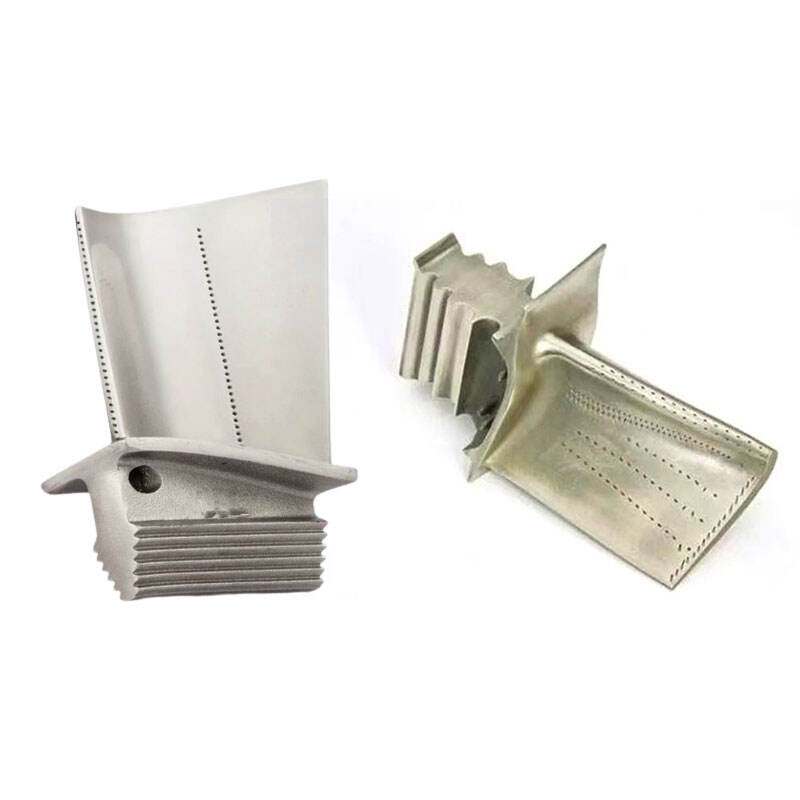

The design and manufacturing of theturbine disk need to ensure that it hassufficient strength and rigidity to withstand thecentrifugal force and inertial force caused byhigh-speed rotation. At the same time, theyneed to be balanced and aligned to ensurestable operation of the turbine.

The turbine blade is the main support structurefor fixed blades. The blades are fixed on the diskto form a rotating blade array. These bladesgenerate power through the impact of airflow,thereby pushing the turbine disk to rotate anddriving related mechanical equipment tooperate.
material
Inconel material Hastelloy material Stellite material Titanium material Nimonic Alloy material
In general, the turbine blade, as one of the core components of the turbine, assumes the important functions ofconnecting, supporting and transmitting power. Its design and manufacturing require precision workmanshipand high-quality materials to ensure efficient, stable and reliable operation of the turbine.
Turbine blade, as a key component of turbines, are widely used in many fields such as aerospace, energy, industry,transportation, and energy extraction, providing power support and energy conversion for various types ofmechanical equipment.
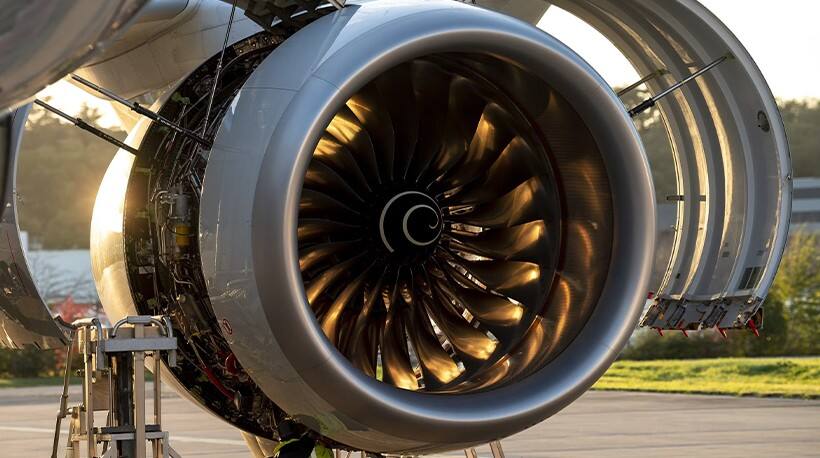

Aerospace field:Turbine discs are widely used in aerospace engines, including jet engines,turbofan engines, etc. They carry the turbine blades, which rotate to drive thecompressor, turbine and other related components to provide power tosupport the flight of the aircraft.

Energy industry:In the energy field, turbine disks are used in steam turbines, gas turbines,steam turbines and other equipment in various types of generating units.They convert gas or steam energy into electrical energy for use in powergeneration plants by turning the rotor of a generator.

Industrial field:In the industrial field, turbine disks are used in various types ofturbomachinery equipment, such as compressors, fans, pumps, etc. Theyrealize the compression, transportation or circulation of fluids or gasesthrough rotation and are used for power transmission and energy conversionin industrial production, manufacturing and processing processes.

Industrial field:In the energy extraction field, turbine disks are used in various turbinemachinery equipment, such as oil and gas extraction equipment,hydroelectric power generation equipment, etc. They drive relatedequipment through rotation to improve energy extraction efficiency andproductivity

Transportation field:Turbine blades are used in turbochargers in automobile engines to improveengine power and fuel efficiency, as well as in turbochargers for transportationvehicles such as trains and ships.

Shipbuilding industry:Turbine blades are used in ship power devices, such as turbochargersand marine turbines, to provide power to drive ships.
Our professional sales team are waiting for your consultation.